Why Large Language Model Optimization Matters Now
Search behaviour is evolving. Instead of typing short keywords into Google, more people are asking conversational questions to tools like ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, and Perplexity.
Below are some commonly asked questions from businesses seeking marketing services. They are not simply searching; they are asking.
- “Can you create a step-by-step plan to grow my SaaS with SEO?”
- “Which agency is best for AI search visibility?”
- “Explain LLMO in simple terms and tell me if my business needs it.”
In many of these moments, users may never see a traditional search results page. They remain inside the AI assistant’s interface, consuming synthesized answers and following the recommendations presented there.
Large Language Model Optimization (LLMO) is about increasing the likelihood that, when those questions are asked, the AI assistant:
- Understands what your business does
- Trusts you as a credible source
- Cites or recommends your content and brand
If SEO is about ranking in search results, LLMO is about being part of the conversation when users speak to AI.
What Is Large Language Model Optimization (LLMO)?
Large Language Model Optimization (LLMO) is the practice of structuring, presenting, and promoting your content and brand so that large language models (LLMs) can:
- Discover your content
- Interpret it accurately
- Use it confidently when generating answers and recommendations.
LLMs include tools such as:
- ChatGPT
- Claude
- Gemini
- Perplexity
- Embedded assistants inside apps, operating systems, and enterprise tools
Traditional SEO asks:
“How do we rank higher in search results for this keyword?”
LLMO adds a new, equally important question:
“When someone asks an AI assistant a question in our domain, what would it take for that assistant to use our content as part of the answer or even recommend our services?”
Key Components of LLMO
Effective LLMO typically combines:
- Topical authority
You publish deep, coherent, and well-organized content on your subject matter, not just isolated posts. - Semantic clarity and structure
Your pages are written and formatted so that machines can easily identify definitions, explanations, steps, and FAQs. - Trust and credibility signals
Your brand appears legitimate and reliable across your website and external platforms, with clear evidence of expertise and a positive reputation.
LLMO does not replace SEO. Instead, it extends SEO into an environment where AI assistants act as gatekeepers to information and recommendations.
LLMO vs SEO vs GEO vs AEO
Because there are multiple acronyms in this space, it is helpful to distinguish them clearly.
- SEO (Search Engine Optimization)
The long-established practice of optimizing content and technical elements so your pages rank higher in traditional search engine results. - AEO (Answer Engine Optimization)
Focuses on structuring content for direct answers, such as featured snippets and “People Also Ask” results. AEO emphasizes clear questions, concise answers, and structured data. - GEO (Generative Engine Optimization)
Focuses on improving how your content is used in AI-generated summaries and overviews, such as Google’s AI Overviews, which combine information from multiple sources into a single response. - LLMO (Large Language Model Optimization)
Focuses on how LLMs themselves interact with your brand and content, whether the model is used:
- Inside a search engine
- In a standalone chat interface
- Embedded within tools, devices, or enterprise platforms
- Inside a search engine
In practice:
- SEO focuses on positions and rankings.
- AEO and GEO is primarily concerned with how your content is used in generative search experiences (such as AI overviews within search engines). LLMO covers a broader scope: how your brand and content are processed, understood, and surfaced by LLMs across search results, chat interfaces, integrated assistants, and beyond. focus on snippets and generative overviews.
- LLMO focuses on how AI systems talk about you and which sources they rely on.
A modern acquisition strategy should treat these as complementary, not competing, disciplines.
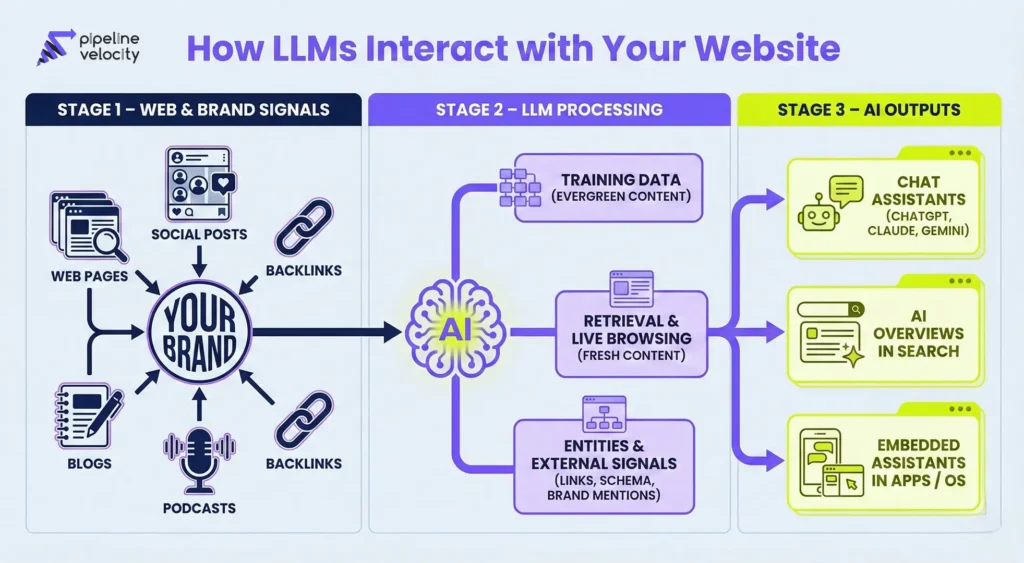
How Large Language Models Interact with Your Content
To optimize for LLMs, you need a realistic understanding of how they work with information.
Training Data
LLMs are trained on vast datasets that may include:
- Public web pages
- Books and technical documents
- Code repositories
- Other large text corpora
This training process builds a general understanding of language and concepts. Well-structured, authoritative content that has existed for some time may already be part of a model’s training data. That means:
- High-quality, evergreen content can shape the model’s internal knowledge.
- Content on domains with strong authority and a clean structure is more likely to shape the model’s understanding of your topic.
Retrieval and Live Browsing
Many modern LLM implementations also use retrieval or live browsing, especially when they need up-to-date or specific information. In those cases, the model:
- Queries the web or a curated index
- Fetches relevant pages or passages
- Uses that information to generate its answer
This is where traditional SEO and technical hygiene intersect strongly with LLMO. If your site is:
- Difficult to crawl
- Poorly organized
- Slow or unstable
Then it becomes harder for retrieval systems to find and use your content reliably.
Entities and External Signals
LLMs do not operate in isolation from the broader web ecosystem. They leverage:
- Links and mentions across other sites
- Consistent brand and entity information
- Structured data, such as schema markup
- Signals of expertise and reputation
All of these help models assess whether your brand is:
- Relevant to a topic
- Trustworthy
- Appropriate to reference or recommend
This is why LLMO is not merely an “on-page” exercise. It includes how you present your brand across the entire digital landscape.
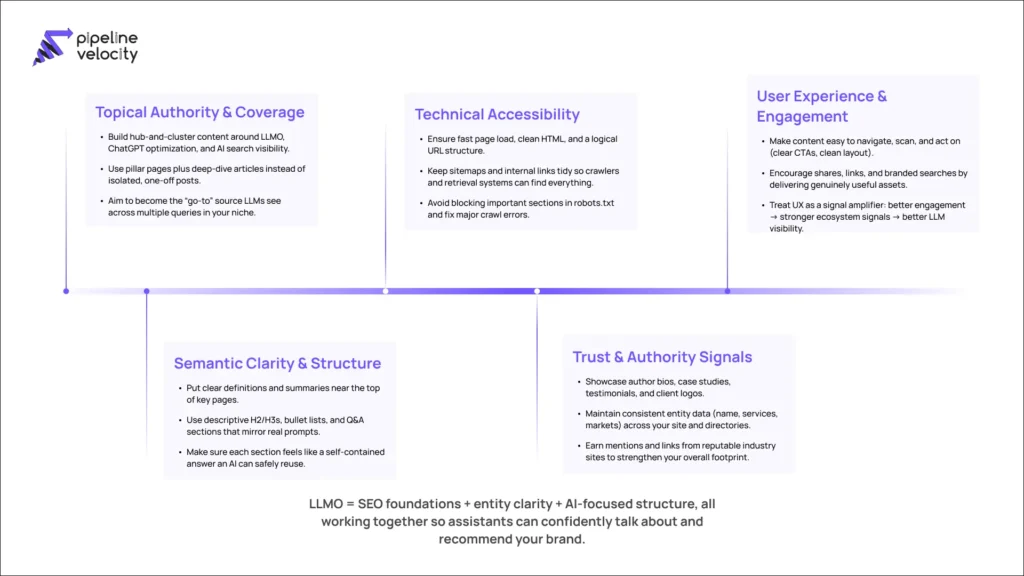
The Five Pillars of LLMO
You can think of LLMO as a system built on five pillars.
Pillar 1: Topical Authority and Coverage
LLMs prefer sources that demonstrate depth and consistency, not isolated content. To build topical authority:
- Develop topic clusters around your main themes.
- Create pillar pages (like a comprehensive LLMO guide) supported by focused articles on subtopics such as:
- ChatGPT optimization
- GEO and AI search visibility
- Technical requirements for LLMO
- Measurement and analytics for AI visibility
- ChatGPT optimization
The objective is to make your site feel like a central hub for key topics rather than a site with just one or two scattered posts.
Pillar 2: Semantic Clarity and Structure
Even advanced models benefit from content that is clearly structured and semantically well defined. This includes:
- Explicit, concise definitions near the top of relevant pages
- Descriptive headings that clearly reflect the content of each section
- Q&A-style sections that mirror how people phrase questions to AI tools
- Bullet points, numbered lists, and frameworks that break down complex ideas
Good structure helps both:
- Human readers quickly scan and understand your content
- LLMs extract coherent, self-contained passages that can be reused in answers.
Pillar 3: Technical Accessibility
Technical fundamentals remain essential. If crawlers and retrieval systems cannot reliably access your content, optimization efforts will have limited impact. Ensure that:
- Your site loads quickly on both desktop and mobile devices
- Key pages are accessible through clean, logical URL structures.
- Your HTML is relatively clean and free of unnecessary complexity.
- XML sitemaps are maintained and up to date.
- Robots.txt does not unintentionally block essential sections.
Technical accessibility is the foundation that allows LLMO and SEO strategies to work effectively.
Pillar 4: Trust and Authority Signals
LLMs are designed to avoid unreliable or misleading information. They are more likely to lean on sources that exhibit clear signs of trust and authority. You can strengthen this by:
- Publishing author profiles with verifiable credentials and experience
- Showcasing case studies, client results, and testimonials
- Securing mentions and coverage from relevant industry publications, partners, and platforms
- Maintaining consistent entity information (name, address, services, markets) across your site and major directories
The more coherent and credible your digital footprint, the easier it is for AI systems to treat you as a dependable reference.
Pillar 5: User Experience and Engagement
While user engagement signals are not the only input to LLMs, they influence the overall health and performance of your site:
- Straightforward navigation helps users and crawlers move through your content logically.
- Clean layouts and accessible design encourage visitors to stay longer and explore more pages.
- Strong content and UX lead to more shares, links, and mentions, essential signals for the broader ecosystem.
A positive user experience indirectly supports LLMO by increasing your content’s reach, impact, and perceived quality.
Step-by-Step LLMO Playbook for Your Website
The following playbook provides a practical approach to implementing LLMO in your organization.
Step 1: Map AI Search Personas and Prompts
Begin by understanding who is likely to use AI tools in your niche and what they are asking.
For example:
- Marketing leaders
- “Design a 90-day LLMO strategy for our B2B SaaS product.”
- “What metrics should I track to measure AI search visibility?”
- “Design a 90-day LLMO strategy for our B2B SaaS product.”
- Founders or business owners
- “Explain LLMO in simple terms. Do I really need it?”
- “How will AI search affect inbound leads for my business?”
- “Explain LLMO in simple terms. Do I really need it?”
- SEO and growth teams
- “How do I audit a website for LLMO readiness?”
- “What is the difference between LLMO, GEO, and traditional SEO?”
- “How do I audit a website for LLMO readiness?”
Action points:
- Identify your key personas.
- For each persona, draft 10–20 realistic prompts they might give to an AI assistant.
- Group these prompts into themes such as definitions, strategy, vendor selection, implementation, and measurement.
These themes will inform the structure of your content hub and supporting articles.
Step 2: Build an LLMO Content Hub
Next, design a hub-and-spoke content structure around LLMO and related topics.
Your hub might include:
- A central pillar page:
- “What Is LLMO? Full Guide to Large Language Model Optimization (2026)”
- “What Is LLMO? Full Guide to Large Language Model Optimization (2026)”
- Additional pillar or deep-dive pages, for example:
- “How to Optimize Your Website for ChatGPT and AI Assistants”
- “LLMO vs GEO vs SEO: When and How to Use Each”
- “How to Optimize Your Website for ChatGPT and AI Assistants”
- Supporting cluster content, such as:
- “Technical Checklist for LLMO and AI Search Visibility”
- “How to Measure AI Search and LLM Visibility”
- “LLMO for Agencies: Getting Recommended by AI Assistants”
- “LLMO for SaaS / Local / Ecommerce: Practical Playbooks”
- “Technical Checklist for LLMO and AI Search Visibility”
Each supporting article should:
- Link back to the relevant pillar page(s)
- Cross-link to related cluster pieces
- Reinforce the same core narrative about what you do and who you serve.
Step 3: Optimize Individual Pages for LLMs
For each significant page in your hub:
- Introduce a clear, concise definition or summary
Start with a short paragraph that explains the page’s core concept or promise in straightforward language. - Add Q&A sections that mirror natural language prompts.
Include headings such as:
- “What is LLMO?”
- “Why is LLMO important in 2026?”
- “How do you implement LLMO on an existing website?”
- “What is LLMO?”
- Use structured formats for complex ideas.
- Step-by-step instructions
- Frameworks and models
- Checklists and best-practice lists
- Step-by-step instructions
- Include concrete examples and scenarios.
For instance, demonstrate how LLMO would apply differently to:
- A SaaS marketing site
- A B2B agency
- A local professional services firm
- A SaaS marketing site
The objective is to create pages that are rich with self-contained, well-structured answers that LLMs can safely use.
Step 4: Implement Structured Data and Entities
Structured data provides valuable context to both search engines and AI systems.
Consider implementing:
- Article schema on blog posts and guides
- FAQPage schema on pages that include Q&A sections
- Organization / LocalBusiness / Service schema for core business and service pages
Include details such as:
- Official business name
- Logo and brand assets
- Contact information and service locations
- Links to essential profiles and listings (social, directories, industry platforms)
Consistent, well-implemented structured data helps both traditional search engines and LLM-based systems build a clearer picture of your brand.
Step 5: Strengthen Off-Site Signals
LLMs draw on the broader web ecosystem, not only your own domain. To strengthen off-site signals:
- Contribute thought leadership articles to relevant industry publications.
- Repurpose key ideas from your LLMO hub into LinkedIn posts, newsletters, and other channels that can attract links and mentions.
- Participate in webinars, podcasts, or panel discussions focused on AI search, LLMO, or GEO.
- Build relationships with complementary tools and platforms for co-created content or partner features.
These activities increase your digital footprint and make your brand more visible to both humans and AI systems.
Step 6: Measure AI Visibility and Iterate
Measurement for LLMO is still emerging, but you can start with a practical approach.
- Manual prompt testing
- On a regular cadence, ask common prompts in tools such as ChatGPT and Perplexity.
- Document whether your brand is mentioned, your URLs are cited, or your frameworks are reflected in the answers.
- On a regular cadence, ask common prompts in tools such as ChatGPT and Perplexity.
- Analytics insights
- Track performance of your LLMO-related content in organic search and referral channels.
- Look for changes in branded search volume for terms related to LLMO and AI search.
- Track performance of your LLMO-related content in organic search and referral channels.
- Content refresh cycles
- Update pillar content every 3–6 months.
- Refresh statistics, screenshots, tool references, and examples as the AI landscape evolves.
- Update pillar content every 3–6 months.
LLMO should be treated as an ongoing process rather than a single campaign.
LLMO Best Practices by Business Type
B2B Services and Agencies
For B2B services and agencies, decision-makers often consult AI assistants for both strategy and vendor evaluation. To position your brand effectively:
- Publish in-depth frameworks and strategic guides, not just surface-level definitions.
- Share case studies that clearly connect your work to measurable business outcomes.
- Offer explanations at multiple levels:
- Executive summaries for non-technical stakeholders
- Detailed implementation guidance for practitioners
- Executive summaries for non-technical stakeholders
- Create content that directly addresses vendor-oriented prompts, such as:
- “What should I look for in an LLMO agency?”
- “How do I evaluate a partner for AI search visibility?”
- “What should I look for in an LLMO agency?”
Sales Pipeline Velocity case study – B2B agency repositioning
A mid-size B2B marketing agency had several disconnected blogs on AI and SEO but wasn’t appearing in AI-driven vendor queries. Sales Pipeline Velocity:
- Consolidated and upgraded their content into a structured “AI Search & LLMO” hub
- Added vendor-focused pages (“How to choose an LLMO agency”, “LLMO services for B2B”)
- Introduced clear executive summaries plus practitioner-level implementation details
Within a few months, the agency started hearing prospects say, “We asked an AI assistant which agencies understand LLMO and your content kept coming up,” leading to a measurable lift in LLMO-qualified discovery calls.
SaaS Companies
SaaS buyers frequently ask AI tools how to solve specific problems or which tools to consider. To adapt:
- Ensure product documentation, help articles, and onboarding guides are detailed and well-structured.
- Provide clear explanations of:
- Core features
- Common use cases
- Integration workflows
- Core features
- Create “how-to” and “comparison” content that helps LLMs surface your product when users ask:
- “What tools help with [specific problem]?”
- “How do I integrate [tool] with [other tool]?”
- “What tools help with [specific problem]?”
Sales Pipeline Velocity case study – RevOps SaaS visibility in AI answers
A RevOps SaaS platform was rarely mentioned when users asked AI tools for “best RevOps tools” or “how to automate revenue reporting.” Sales Pipeline Velocity:
- Mapped 50+ realistic AI prompts from RevOps leaders and sales teams
- Rebuilt the site around use-case and integration pages aligned to those prompts
- Tightened product docs and created “how-to” guides that explained real-world workflows
As a result, AI assistants began citing the brand more often in tool recommendation answers, and the client saw a steady rise in trials where users mentioned, “We found you while asking ChatGPT how to solve X.”
Local and Regional Businesses
Local businesses may see AI assistants replacing or supplementing “near me” searches. To prepare:
- Maintain strong local SEO fundamentals (e.g., Google Business Profile, local citations, reviews).
- Create pages that clearly describe:
- Services offered
- Service areas and locations
- Typical customer profiles
- Services offered
- Encourage reviews that mention:
- The service provided
- The location
- The specific outcome or benefit
- The service provided
This type of information is highly useful when AI systems answer local intent queries.
Sales Pipeline Velocity case study – Multi-location service provider
A regional professional services business with multiple locations was inconsistently represented online, leading to confusing AI answers for “best [service] near me”. Sales Pipeline Velocity:
- Standardized NAP and service information across the website and major directories
- Created location-specific service pages with clear, descriptive copy
- Launched a simple review strategy encouraging customers to mention service type and city
Over time, AI assistants started returning more accurate, location-aware recommendations that prominently included the client, and they reported an increase in inbound calls where prospects said, “You were suggested when I asked an AI for [service] in [city].”
Common LLMO Mistakes to Avoid
As you develop your LLMO strategy, be mindful of these frequent pitfalls:
- Treating LLMO as keyword stuffing with AI phrases
Simply adding “LLMO” or “ChatGPT optimization” to existing content without structural or strategic change will not achieve meaningful results. - Publishing generic AI-themed content without genuine expertise
Shallow or derivative articles on “AI and SEO” can dilute your brand and may even reduce trust. - Ignoring technical issues
Slow, unstable, or poorly structured sites make it difficult for retrieval systems and crawlers to access your content effectively. - Relying on one isolated LLMO article
A single blog post is not enough to establish authority. A cluster of related, well-organized content is far more valuable. - Failing to test how AI tools already answer questions in your domain
Without regular prompt testing, you lack visibility into your current position in the AI ecosystem.
FAQ: LLMO, ChatGPT Optimization, and AI Search
Q1. Is LLMO just another name for SEO?
No. LLMO builds on SEO but has a different focus. SEO is primarily about improving a page’s position in search results. LLMO is about improving how AI assistants understand, reference, and potentially recommend your brand when answering questions.
Q2. Do I still need traditional SEO if I invest in LLMO?
Yes. Traditional SEO remains essential. Strong technical foundations and content that rank well in organic search often serve as the raw material that LLMs and generative search systems rely on. LLMO and SEO are complementary.
Q3. How long does it take to see an impact from LLMO?
Timelines vary by market and starting point, but you can think in similar terms to SEO. Structural improvements and new content can begin to show early signs of impact within a few weeks. Still, meaningful gains in authority and recognition by AI systems typically take 3–6 months or more of consistent effort.
Q4. Is LLMO only relevant for large brands?
No. Smaller brands can benefit significantly, particularly in focused niches where high-quality content is limited. If you become one of the few trustworthy, well-structured sources in your niche, you can gain outsized visibility in AI-generated answers.
Q5. How is LLMO different from GEO (Generative Engine Optimization)?
GEO is primarily concerned with how your content is used in generative search experiences (such as AI overviews within search engines). LLMO covers a broader scope: how your brand and content are processed, understood, and surfaced by LLMs across search results, chat interfaces, integrated assistants, and beyond.
Next Steps: Building Your LLMO Roadmap
LLMO is still an emerging discipline, but the direction of search and discovery is clear: AI assistants are becoming a core interface between people and information.
A practical next step is to:
- Audit your current site for topical authority, structure, and technical readiness.
- Define a clear content hub around LLMO and related topics.
- Implement a consistent but straightforward measurement and refresh process.
From there, you can expand deeper into:
- LLMO-driven editorial planning
- AI visibility monitoring
- Integration of LLMO with your broader SEO and growth strategy
Done well, LLMO does not just increase traffic; it positions your brand to be present in the high-intent, AI-mediated conversations that increasingly shape buying decisions.




